Positive Displacement Pumps | PD Pumps
Positive displacement pumps, or PD pumps, are a form of vacuum pump that creates a consistent flow of fluids that moves liquids at a steady speed through the system. PD pumps are capable of moving a variety of fluids like slurry and sludge, muds, oils, chemicals, pulps, pastes, wastes, foods, and other liquids. Positive displacement pumps operate by using a mechanism or mechanisms to create a suction or vacuum that draws in and captures the fluid in its chamber before passing it through. A positive displacement pump is ideal for higher viscosity liquids that are transported at a lower flow rate but at a higher pressure. Positive displacement pumps tend to fit into two main classifications, rotary and reciprocating pumps. Each includes multiple variations of pumps that are identified by the mechanism they use for moving the fluids.
Rotary pumps use a rotating mechanism to create suction, while the mechanisms on reciprocating pumps move in a back-and-forth action. The rotary pump types use gears, lobes, vanes, and screws for moving fluids. Reciprocating positive displacement pumps use diaphragms, pistons, and plungers. The different types of PD pumps all have applications that they work best in, and they also provide excellent pumping in a variety of other cross applications.
DAE Pumps manufactures a variety of different types of top-rated positive displacement pumps. Our large selection of affordable heavy-duty PD pumps last, giving you the complete peace-of-mind. The expert team at DAE Pumps is available to help you select the right type and size pump that works for your project. Contact us today!

Rotary Pumps
A rotary positive displacement pump works to provide consistent movement of sludge, slurry, thick mud, chemical, solids, and a variety of mixed fluids and solids. Let us help you select the gear, lobe, vane, screw, twin-screw or diaphragm pump that is right for your application need, as we specialize in rotary positive displacement pumps.
Reciprocating Positive Displacement Pumps
Reciprocating positive displacement pumps repeat a back-and-forth movement that draws the fluid pumped into a chamber then pushes them out the other end. The high viscosity fluids are suctioned in then rapidly pushed out. This repeated pumped fluid action can cause strong vibrations in the pump during operation, but DAE Pump heavy-duty pump casing minimizes the vibrations for smooth operations. Once the highly viscous fluids or material is suctioned into the chamber through the pump inlet, the valve closes and doesn’t allow the pumped fluid back out. When the pump pushes the liquids out, the valve around the outlet opens for the pumped liquid to flow out the discharge or outlet end. We provide piston and diaphragm pumps for large scale industrial operations.
Diaphragm Pumps:
A diaphragm pump uses a flexible membrane that expands the fixed volume of the pumping chamber, bringing in the fluid by opening the inlet valve, then compressing it to high pressures to push out the materials through the outlet valve. DAE Pumps diaphragm pumps are hermetically sealed, making them safe for pumping hazardous, corrosive and shear sensitive fluids. They also work well in water treatment, paints, oils, metering, dispensing. Unlike centrifugal pumps, diaphragm pumps are self-priming and are excellent for working with low flow applications that need high-pressure output.
Air Operated Diaphragm Pumps
Air operated diaphragm pumps, also known as AODD pumps, are reciprocating pumps that operate using compressed air as their power source. These positive displacement pumps feature two diaphragms that reciprocate back and forth, creating a pumping action. As compressed air is supplied to one of the diaphragms, it pushes the diaphragm outward, simultaneously drawing liquid into the opposite chamber through a suction valve. Once the diaphragm reaches the end of its stroke, an air valve mechanism redirects the compressed air to the second diaphragm, causing it to push the liquid out of the discharge chamber.
This continuous alternation between the two diaphragms ensures a steady, constant flow of liquid. The design of an air operated diaphragm pump allows it to handle a variety of fluids, including high viscosity fluids, abrasive materials, or those that contain solids, making this type of diaphragm pump versatile and reliable for numerous industrial applications where centrifugal pumps fail.

Piston Pumps:
The piston pump is a positive displacement pump that uses a piston to draw in liquids and solids by creating a vacuum in the chamber to suction in the materials, then pushing them out the other end. The piston repeatedly moves up and down inside the pump chamber to pump the material. The DAE Pumps piston pump uses high-quality O-rings to ensure reliable performance and constant flow and fluid pressure. These positive displacement pumps can be used for high-pressure washing, oil production, paint spraying, and other low viscosity liquids.

Rotary Positive Displacement Pumps
Rotary positive displacement pumps use cogs and gears to force liquids and solids through the pump. The rotating gears or cogs create a seal with the pump casing that causes suction. The material is drawn into the pump housing and enclosed between the teeth of the rotation gears/cogs and then transferred to the outlet. DAE Pumps provides multiple types of rotary pumps like gear pumps, lobe pumps, vane pumps, screw pumps, and twin-screw pumps.
Gear Pumps:

Gear pumps (and internal gear pumps) are one of the most common types of positive displacement pumps. They provide a constant volume of fluid that passes between the teeth of two meshing gears and the pump casing. The rotating gears and separation of teeth create a suction that pulls fluid in through the inlet. The gears then trap the liquid and move it around the casing to the discharge or outlet. Each revolution creates steady flow of fluid.
There are two main types of rotary gear pumps, internal and external. Both of these positive displacement pumps work using similar principles for pumping fluids. Two gears are inside a casing in a way that the teeth lock together. As a motor turns one of the gears, the locking teeth turn the other. The difference in the two designs is that an external gear pump uses side-by-side gears (typically the same size), so when the motor turns one gear, the other rotates in the opposite direction. The internal gear pump operates using two different size gears. A motor turns the small gear, which is inside the larger gear, rotating it in the same direction.
DAE Pumps offers economical rotary gear pumps of both types in a variety of sizes. No other gear pumps can match the performance and durability of our pumps. Because of the close tolerance between the gears and casing, most gear pumps are highly susceptible to wear, but DAE Pumps gear pumps outperform all others with limited pump slip. Our pumps process a wide range of high and low viscosity fluids and are ideal for handling fluids at high pressures and low flow rates. DAE Pumps rotary gear pumps are widely used in chemical installations to pump highly viscous fluids. They are one of the most common positive displacement pump types for moving corrosive liquids and hydraulic fluid power applications.
DAE pumps gear pumps provide consistency in moving a variety of slurry materials and are suitable for several industries like paints, food processing, chemicals, oil & gas, and others. Our rotary gear pumps are available in duplex steel, cast steel, and cast iron, among other materials. Contact DAE Pumps to customize a positive displacement pump to your specific needs.

Internal Gear Pump

External Gear Pump
Lobe Pumps:

Lobe pumps are like gear pumps in that fluid flows around the interior of the casing, but they use lobes instead of the gears with teeth. The lobes do not touch each other, thus reducing wear, and they are driven by external timing gear which can allow the lobe pump to operate in either direction.
A rotary lobe pump is capable of handling thick fluids that are laden with solids, but does require a pressure relief valve. The rotary lobe pump offers gentle handling of solids that work well mixed with low viscosity fluids, making them a preferred positive displacement pump for food and wine producers and manufacturers. The DAE Pumps positive displacement lobe pumps for these industries offer quick-release fasteners for easy access to the inlet valve, pressure relief valve, outlets, fitting, and lobes for cleaning and sanitizing.
In addition to the food and beverage industries, DAE Pumps lobe pumps applications include pulp and paper, oil, gas, chemical, pharmaceutical, wastewater, biotech other industries. These rotary lobe pump types are lined with an elastomer to protect the internal spacing within the pump casing. Of note is that because of the way this positive displacement pump works, multi-lobe pumps can significantly reduce vibration.

Vane Pumps:

A vane pump uses blades, know as vanes, that slide in and out of rotor slots to move fluids. The action creates a suction that pumps fluids. A vane pump uses multiple sets of vanes that mount on an off-center rotor that sits close to the cam wall. This creates a crescent-shaped cavity on the other side. The blades, which are always in contact with the cam wall, turn with the rotor. As the rotor spins, the vanes slide out when they reach the cavity, trapping fluid. As the vanes reach the end of the open space, they slide back in, and the trapped fluid then to the outlet or discharge valve. The DAE Pumps vane pumps are used in automotive, fuel loading and transmission, drink dispensing, and other industries.

Screw Pumps:
Screw pumps and twin-screw pumps use rotating screws to move liquids and solids from one end of this type of positive displacement pump to the other. The turning action creates a spinning motion that pumps material. The twin-screw pumps are identical to the screw pump, but with a dual screw for more power, which also ensures they can work with any fluid viscosity. Screw pumps are capable of high flow rates with very little to no vibration and high pump efficiency. A screw pump provides excellent efficiency in irrigation, oil production, fuel injection, and fuel transfer, among other positive displacement pumps applications.
Progressive Cavity Pump Features
Progressive cavity pumps, also known as eccentric screw pumps, operate based on the positive displacement principle using a helical rotor and a stator to move fluid. In a progressive cavity pump the rotor, typically made of metal, has a helical shape and rotates within a stator, which is usually made of an elastomeric material and has a double helix configuration.
As the rotor turns, it creates a series of sealed cavities or chambers between the rotor and the stator. These cavities move progressively from the suction side to the discharge side of the progressive cavity pump. When a cavity forms at the suction end, it creates a low-pressure area that draws the fluid into the cavity. As the rotor continues to turn, the fluid-filled cavity moves along the length of the pump, transporting the fluid toward the discharge end. This continuous movement of cavities ensures a smooth, non-pulsating flow of fluid.
Progressive cavity pumps are particularly effective for handling viscous, shear-sensitive, or abrasive fluids, as well as fluids containing solids. They are widely used in industries such as wastewater treatment, oil and gas, food and beverage, and chemical processing. Their ability to maintain a consistent flow regardless of the fluid’s viscosity or pressure makes them ideal for applications requiring precise metering and dosing. Additionally, their design minimizes shear forces, making them suitable for delicate or sensitive fluids. The robust construction and versatility of progressive cavity pumps contribute to their reliability and long service life in demanding industrial environments.

Peristaltic Pumps (or Tube Pumps)
Peristaltic pumps, also known as hose or tube pumps, are a positive displacement pump that operates using a simple but effective mechanism that mimics the natural peristalsis process found in biological systems. A peristaltic pump consists of a flexible tube or hose and a series of rollers or a rotor. As the rotor in a peristaltic pump turns, the rollers compress the tube, creating a seal that traps the fluid within the tube. This compression moves along the length of the tube, pushing the fluid forward. Once the rollers pass, the tube returns to its original shape, creating a vacuum to increase fluid pressure that draws in more fluid from the inlet.
This continuous sequence of compression and relaxation results in a smooth, pulsation-free flow. Peristaltic pumps are particularly valued for their ability to handle a wide range of fluids, including those that are viscous, shear-sensitive, or contain particulates, as the fluid only contacts the inner surface of the tube, minimizing contamination and ensuring gentle handling. Their simple design also makes them easy to maintain, as the tubing can be quickly replaced without the need for extensive disassembly.
Plunger Pumps
Plunger pumps, a type of pd pump, are designed to handle high-pressure, constant flow applications with precision and reliability. A plunger pump operates using a reciprocating plunger or piston mechanism to move fluid through the pump. This type of reciprocating pump consists of a pump cylinder, a plunger that moves back and forth within the cylinder, and a set of check valves to control the flow of the fluid.
When the plunger retracts within a plunger pump, it creates a vacuum within the cylinder, causing the inlet check valve to open and allowing fluid to be drawn into the cylinder. As the plunger moves forward, it compresses the fluid, closing the inlet check valve and opening the discharge check valve, forcing the fluid out of the cylinder and into the discharge line. This cycle of suction and discharge continues, providing a steady, pulsating flow of fluid, often at constant pressure.
Plunger pumps are capable of producing very high pressures and are highly efficient, making them ideal for applications such as hydraulic systems, water jetting, and oil and gas operations, as well as dosing and metering applications. They are also well-suited for handling a wide range of fluids, including those with high viscosities and abrasive or corrosive properties. Plunger pump design allows for precise control over the flow rate and pressure, and their robust construction ensures durability and long service life, even under demanding conditions.
The DAE Pumps Advantage

With over 30 years of experience in pump designing and engineering, DAE Pumps keeps your pumping needs in mind. We provide a variety of affordable heavy-duty pumps that are used in various industries and for a wide array of applications. Not all applications are the same, so not all pumps should be the same. Our experienced team can help you select the right pump per your requirement. We also offer custom pump designs.
DAE Pumps provides cost-efficient durable pumps that last. Our pumps undergo extensive testing and quality control to ensure you get a reliable, worry-free pump that does the job you need. Rely on DAE Pumps for in-stock pumps, dredging equipment, and other product that are ready-to-ship.
You can trust DAE Pumps!
PD Pump Advantages
Depending on the use and application, positive displacement pumps can hold a distinct advantage over centrifugal pumps. The mechanical movement of fluid by displacement does have certain benefits over the centrifugal action:
- PD Pumps handle viscous fluids with ease
- Much more controllable consistent flow of fluids. Double the output by doubling the size and speed
- Pump speeds can be low, making them controllable, smooth, and less disruptive
- The action makes positive displacement pumps self-priming
- The discharge pressure can be very high, subject to the motor power, casing strength, shaft sealing, and volumetric efficiency
- The net positive suction head required (NPSHR) is low, making them very useful where there is little net positive suction head available (NPSHA)
- PD Pumps are bidirectional, meaning they can pump in both directions, forward and backward.
Accessories
DAE Pumps offers a variety of accessories for all your project needs. We stock multiple sizes of slurry hoses, ultrasonic flow meters for ensuring optimal pumping performance, or hydraulic power units for powering up your operations. All our parts are always in stock and available for immediate shipping to anywhere in the US and the world. Contact a DAE Pumps representative today!
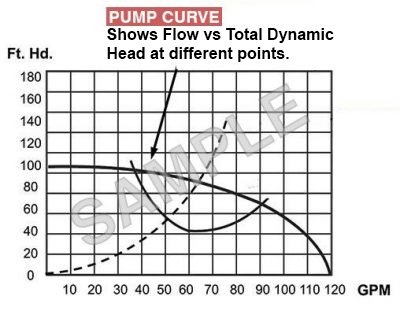
Custom Pump Curve
A pump curve is a graphical representation of a pump’s flowrate against a certain level of the head. Using a pump curve that is specific for your application will greatly help in selecting the pump best for you, ultimately saving you time and money.
Pump curves data gathered during testing of the pump’s performance at the manufacturer’s facility and provide the end-user with a graph of how the pump will operate over a set range. To build the pump curve, our engineers compile several variables, including the type of material, fluid viscosity, distance to pump, target GPM, and job-specific factors. This ensures the most efficient pump is recommended for your project.
Get in Touch
Positive Displacement Pumps FAQs
What is a positive displacement pump?
A positive displacement pump is a type of pump that moves fluid by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and then forcing it into the discharge pipe. Unlike dynamic pumps, which rely on centrifugal force, positive displacement pumps provide a constant flow rate regardless of changes in pressure.
What are the different types of positive displacement pumps?
Positive displacement pumps come in various types, including rotary pumps (such as gear pumps, screw pumps, and rotary vane pumps) and reciprocating pumps (such as piston pumps and diaphragm pumps). Each type has its unique mechanism for displacing fluid and is suitable for different applications and operating conditions.
How does a positive displacement water pump work?
A positive displacement water pump operates by trapping and transferring a fixed volume of water with each cycle of operation. For example, in a reciprocating piston pump, the piston moves back and forth within a cylinder, drawing in and expelling water through valves. In a rotary gear pump, intermeshing gears trap water and transfer it from the inlet to the outlet as they rotate.
What are the advantages of using a small positive displacement pump?
Small positive displacement pumps offer several advantages, including precise flow control, high efficiency, and suitability for low-flow and high-pressure applications. Their compact size makes them ideal for applications where space is limited or portability is required, such as in laboratory equipment, medical devices, and small-scale industrial processes.
What are some common applications of positive displacement pumps?
Positive displacement pumps are used in a wide range of industries and applications, including chemical processing, food and beverage production, pharmaceutical manufacturing, oil and gas extraction, wastewater treatment, and HVAC systems. They are ideal for pumping viscous fluids, abrasive slurries, and fluids with variable flow rates or pressures.
How do I select the right positive displacement pump for my application?
Selecting the right positive displacement pump involves considering factors such as the type of fluid being pumped, flow rate and pressure requirements, temperature and viscosity of the fluid, and compatibility with system components. Consulting with a dredging and industrial pump expert can help you choose the appropriate pump type and configuration for your specific application and ensure optimal performance and reliability.